Psychometrics Explained
Psychometrics is concerned with the measurement of psychological variables such as personality or, in the case of me2, creativity. If you like, it attempts to provide the equivalent of a ruler, but instead of measuring height, psychometrics is used to measure psychological variables.
There are many psychometric methods, but certainly for the development of the General Factor of Creativity model (me2), the most important of these is a method called Factor Analysis.
What is Factor Analysis?
Historically, Charles Spearman is credited with developing the first Common-Factor-Analysis model. Spearman examined the test scores of 36 boys on topics such as Classics, French, English, Mathematics, Discrimination of Tones and Weight. He had a theory that underlying these scores was a general ability, plus abilities specific to each topic. In terms of Factor Analysis, he proposed that there was one general factor underlying human cognitive abilities, which in everyday terms we would call intelligence.
The Factor Analysis method allows us to answer a number of questions:
- How many different things are measured by the scores?
- What is measured by the scores?
- How are these different things related?
- How well are these things measured?
Below is an example of a Factor Analysis:
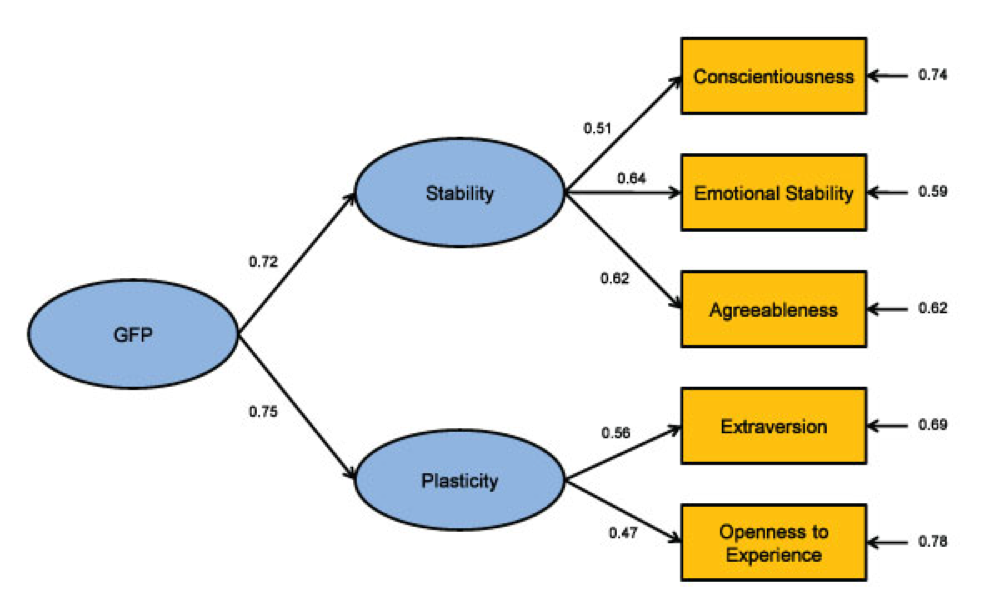
In this example, there are five scores on Conscientiousness, Emotional Stability, Agreeableness, Extraversion and Openness-to-Experience. According to the model, these scores measure two things (Factors) which are labelled Stability and Plasticity. In turn, Plasticity and Stability are related, since they are explained by one general factor. An index of how well these factors are measured is provided by the factor loadings, for example, Conscientiousness loads at 0.51 on Stability. These factor loadings vary from a score of zero to one, the closer the loadings are to one, the better the quality of measurement. Equally, the higher the loading score of a factor, the more indicative it is of what the factor measures, so Emotional Stability is the most important component of Stability as it has the highest factor loading score.
These are some of the very basic principles of Factor Analysis which we used to develop the General Factor of Creativity (me2). If you wish to know more about Factor Analysis you can listen to my talk on what is Factor Analysis.
If you are even more interested then you might find the following references useful:
Kline, R. B. (2005). Principles and Practice of Structural Equation Modelling. London: The Guilford Press.
Brown, T. A. (2006). Confirmatory factor analysis for applied research. New York, N.J.: Guilford Press.